Radon in Your Home
General Radon
Information:
Radon is a
carcinogenic gas that is
hazardous to inhale. Build-up of radon in homes is a health concern and
many lung cancer cases are attributed to radon exposure each year.
About 12% of lung cancers > more than 22,000 Americans die of
radon-related lung cancer each year. 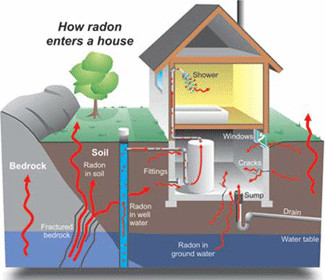 The
Surgeon General of the United States has issued a Health Advisory
warning Americans about the health risk from exposure to radon in
indoor air. The Surgeon General urged Americans to
test
their homes to find out how much radon they might be
breathing.
He also stressed the need for them to remedy the problem as
soon as possible.
The
Surgeon General of the United States has issued a Health Advisory
warning Americans about the health risk from exposure to radon in
indoor air. The Surgeon General urged Americans to
test
their homes to find out how much radon they might be
breathing.
He also stressed the need for them to remedy the problem as
soon as possible.
You cannot
see, smell
or taste
radon, but it still may be a problem in your home. When you
breathe air containing radon, you increase your risk of getting lung
cancer. In fact, the Surgeon General has warned that
radon
is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States
today. If you smoke and your home has high radon levels, your
risk of lung cancer is especially high. Every home has some
level
of radon. Many states require radon testing for all homes
being
sold. Idaho does not yet require it.
Testing is the only
way to find out your home's radon levels
The EPA and the Surgeon General
recommend testing all homes for radon. Radon has been found in homes
all over the United States. It comes from the natural breakdown of
uranium in soil, rock and water and gets into the air you breathe.
Radon typically moves up through the ground to the air above and into
your home through cracks and other holes in the foundation. Your home
can trap radon inside. Radon can also enter your home through well
water. If you find that you have high
radon levels,
there are always ways to fix a
radon problem.
Even very high levels can be reduced to
acceptable levels... often
at very low, or no cost.
Any home can have a radon problem. This
means new
and old homes,
well-sealed and drafty homes, and homes with or without basements. In
fact, you and your family are most likely to get your greatest
radiation exposure right at home. That is where you spend most of your
time.
Nearly 1 out of every 15 homes in the United States is estimated to
have an elevated radon level. Boise and Valley counties are much
higher, while Gem county is much lower. Elevated levels of
radon gas have been
found in homes in Idaho. In fact, homes in Boise and Valley
counties have been recorded as containing some of the highest radon
levels in the entire country.
EPA's Radon Testing Check List:
-
Notify the
occupants of the
importance of proper testing conditions. Give the occupants written
instructions or a copy of this Guide and explain the directions
carefully.
-
When doing a
short-term test
ranging from 2-4 days, it is important to maintain closed-house
conditions for at least 12 hours before the beginning of the test and
during the entire test period.
-
When doing a
short-term test ranging from 4-7 days, EPA recommends that closed-house
conditions be maintained.
-
If you hire
someone to do the
test, hire only a qualified individual. Some states issue
photo
identification (ID) cards; ask to see it (Idaho does not, but I am
nationally certified and I do have this ID).
The
tester's ID number, if available, should be included or noted in the
test report.
-
The test should
include method(s) to prevent or detect interference with testing
conditions or with the testing device itself.
-
If the
house has
an active
radon-reduction system, make sure the vent fan is operating
properly. If the fan is not operating properly, have it (or
ask
to have it) repaired and then run the test.
If your
home has not
yet been
tested for Radon, have a test taken as soon as possible. If you can,
test your home before putting it on the market. You should
test
in the lowest level of the home which is suitable for occupancy. This
means testing in the lowest level that you currently live in or a lower
level not currently used, but which a buyer could use for living
space.
The radon
test result reveals important
information about your home's radon level. Some states
require
radon measurement testers to follow a specific testing
protocol.
If you do the test yourself, you should carefully follow the testing
protocol for your area or EPA's Radon Testing Checklist. If
you
hire a contractor to test your residence, protect yourself by
hiring a qualified individual
or company. Oxbow
is one such company. Others can be found on the National
Radon Safety Board (NRSB) registry (there are
no others in Idaho. I am it). I
have completed courses in formal radon education, and I am
certified by the National Radon
Safety Board. I use the very latest in portable high
technology instruments
available: the RAD-7 from
Durridge, and I test every home for radon as part of
my basic
home inspection, at no additional
cost.
Most states can provide you with a list of knowledgeable radon service providers doing business in the state. In states that don't regulate radon services (Idaho does not), ask the contractor if he holds a professional proficiency or certification credential. Such programs usually provide members with a photo-ID card which indicates their qualification(s) and its expiration date. If in doubt, you should check with the organization that issue the credential. Alternatively, ask the contractor if they've successfully completed formal training appropriate for testing or for mitigation, e.g., a course in radon measurement or radon mitigation. There is only one company within 200+ miles of Boise that is certified in Radon Testing and performs Radon Mitigation. They are real pros and do exceptionally fine work. They are called "Idaho Radon". They can be contacted at:
Idaho Radon
Office phone: 208.994.9655
Please visit their web site at: www.idahoradon.com
If you are thinking of selling your home and you have already tested your home for radon, provide your test results to the potential buyer.
Radon
Myths and Facts
MYTH:
Scientists are
not sure that radon really is a problem.
FACT:
Although
some scientists dispute the precise number of deaths due to radon, all
the major health organizations (like the Center for Disease Control and
Prevention, the American Lung Association and the American Medical
Association) agree with estimates that radon causes thousands of
preventable lung cancer deaths every year. This is especially true
among smokers, since the risk to smokers is much greater than to
non-smokers.
MYTH:
Radon testing
is difficult, time-consuming and expensive.
FACT:
Radon testing is easy and
inexpensive.
MYTH:
Radon testing
devices are not reliable and are difficult to find.
FACT:
Reliable testing devices are available
from qualified radon testers and
companies.
MYTH:
Homes with
radon problems can't be fixed.
FACT:
There are
simple solutions to radon problems in homes. Hundreds of thousands of
homeowners have already fixed radon problems in their homes. Radon
levels can be readily lowered for $800 to $2,500 (with an average cost
of $1,200). Often, radon levels can be "fixed" simply by
making
some simple ventilation adjustments.
MYTH:
Radon affects
only certain kinds of homes.
FACT:
House
construction can affect radon levels. However, radon can be a
problem in homes of all types: old homes, new homes, drafty
homes, insulated homes, homes with basements and homes without
basements. Local geology, construction materials, and how the
home was built are among the factors that can affect radon levels in
homes.
MYTH:
Radon is only a
problem in certain parts of the country.
FACT:
High radon
levels have been found in every state. Radon problems do vary from area
to area, but the only way to know your radon level is to test.
MYTH: A
neighbor's
test result is a good indication of whether your home has a problem.
FACT:
It's not.
Radon levels can vary greatly from home to home. The only way to know
if your home has a radon problem is to test for it.
MYTH: It's
difficult
to sell a home where radon problems have been discovered.
FACT:
Where
radon problems have been fixed, home sales have not been blocked or
frustrated. The added protection is sometimes a good selling point,
making it easier
to sell.
MYTH: I've
lived in
my home for so long, it doesn't make sense to take action now.
FACT:
You will
reduce your risk of lung cancer when you reduce radon
levels, even if you've lived with a radon problem for a long
time.
MYTH:
Short-term tests
can't be used for making a decision about whether to fix your home.
FACT:
A
short-term test, followed shortly by a second short-term test can be
used to decide whether to fix your home, or whether additional testing
is required. However, the closer the average of your two short-term
tests is to 4 pCi/L (Pico Curies per Litre), the less certain you can
be about whether your year-round average is above or below that
level. Keep in mind that radon levels below 4 pCi/L still pose
some
risk. Radon levels can be reduced in most homes to 2 pCi/L or
below.
Radon
In Idaho
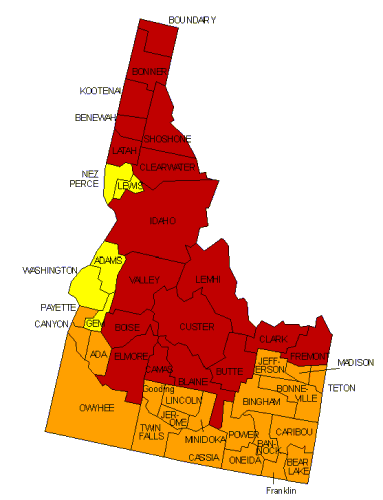
Homes
with elevated levels of radon have been found in Idaho in all three
zones. All homes should be tested regardless of their geographic
location. Important points to note:
- All homes should test for radon,
regardless of their geographic location or zone
-
There
are many thousands of individual homes with elevated radon levels in
Zones 2 and 3. Elevated levels can be found in Zone
2 and Zone 3 counties.
-
All
users of this map should carefully review the map documentation for
information on within-county variations in radon potential and
supplement the map with locally available information before making any
decisions.
-
The
map is not to be used in lieu of testing during real estate
transactions.
The Map was
developed
(by the EPA) using 5 factors to determine radon potential: indoor radon
measurements; soil permeability; geology; foundation
type;
and aerial radioactivity. Radon potential assessment is based upon
known geologic provinces. Geologic Provinces were adapted to
county boundaries for the Map of Radon Zones.
Sections
307 and 309 of the Indoor Radon Abatement Act of 1988 (IRAA) directed
the EPA to list and identify areas of the U.S. that have the potential
for elevated indoor radon levels. Thie EPA's Map of Radon
Zones assigns each of the 3,141 counties in the U.S. to one of three
zones based on radon their individual potential:
 |
Zone
1 counties have a predicted average indoor radon screening
level greater than 4 pCi/L (pico curies per liter) (red zones)
|
Highest
Potential |
 |
Zone
2 counties have a predicted average indoor radon screening
level between 2 and 4 pCi/L (orange zones) |
Moderate
Potential |
 |
Zone
3 counties have a predicted average indoor radon screening
level less than 2 pCi/L (yellow zones) |
Low
Potential |
Radon gas
decays
naturally into radioactive particles that can get trapped in your lungs
when you breathe. As they break down further, these particles
release small bursts of energy. This can damage lung tissue and can
lead to lung cancer at some time during the course of your
lifetime. Not everyone who is exposed to elevated levels of
radon
will develop lung cancer. And the amount of time between the actual
exposure and the onset of the disease may in fact be many years.
Just like
many other
environmental pollutants, there is some uncertainty about the magnitude
of the health risk posed by Radon. However, we do know more about the
risks from Radon than we do about risks from most other cancer-causing
substances. This is because our estimates of cancer risks from
Radon are actually based on studies of cancer in humans (underground
miners) rather than merely laboratory controls such as mice etc.
Smoking
tobacco, when combined with Radon is an especially serious health risk.
Stop smoking and you will immediately lower your lung cancer
risk from Radon exposure.
Children
have been reported to have greater risk than adults of certain types of
cancer from radiation, but there are currently no conclusive data on
whether children are at greater risk than adults from Radon.
Your chances of
getting lung cancer from radon depend mostly on:
- How much radon is in
your home
- The amount of time you
spend in your home
- Whether you are a
smoker or have ever smoked
Radon Risk If You Smoke:
| Radon
Level |
If
1,000 people who smoked were exposed to this level over a lifetime*... |
The
risk of cancer from radon exposure compares to**... |
WHAT
TO DO:
Stop smoking and... |
| 20 pCi/L |
About 260 people could get lung cancer |
250 times the risk of drowning |
Fix your home |
| 10
pCi/L |
About 150
people could get lung cancer |
200 times
the risk of dying in a home fire |
Fix your home |
| 8 pCi/L |
About 120 people could get lung cancer |
30 times the risk of dying in a fall |
Fix your home |
| 4
pCi/L |
About 62
people could get lung cancer |
5 times the
risk of dying in a car crash |
Fix your home |
| 2 pCi/L |
About 32 people could get lung cancer |
6 times the risk of dying from poison |
Consider fixing between 2 and 4 pCi/L |
| 1.3
pCi/L |
About 20
people could get lung cancer |
(Average
indoor radon level) |
(Reducing
radon
levels below 2 pCi/L is difficult.) |
| 0.4 pCi/L |
About 3 people could get lung cancer |
(Average outdoor radon level) |
Note: If you are a
former smoker, your risk may be lower.
* Lifetime risk of lung cancer deaths from EPA Assessment of Risks from
Radon in Homes (EPA 402-R-03-003).
** Comparison data calculated using the Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention's 1999-2001 National Center for Injury Prevention and
Control Reports. |
Radon
Risk If You've Never Smoked:
| Radon
Level |
If
1,000 people who never smoked were exposed to this level over a
lifetime*... |
The
risk of cancer from radon exposure compares to**... |
WHAT
TO DO: |
| 20 pCi/L |
About 36 people could get lung cancer |
35 times the risk of drowning |
Fix your home |
| 10
pCi/L |
About 18
people could get lung cancer |
20 times the
risk of dying in a home fire |
Fix your home |
| 8 pCi/L |
About 15 people could get lung cancer |
4 times the risk of dying in a fall |
Fix your home |
| 4
pCi/L |
About 7
people could get lung cancer |
The risk of
dying in a car crash |
Fix your home |
| 2 pCi/L |
About 4 person could get lung cancer |
The risk of dying from poison |
Consider fixing between 2 and 4 pCi/L |
| 1.3
pCi/L |
About 2
people could get lung cancer |
(Average
indoor radon level) |
(Reducing
radon levels below
2 pCi/L is difficult.) |
| 0.4 pCi/L |
|
(Average outdoor radon level) |
Note: If you are a
former smoker, your risk may be higher.
* Lifetime risk of lung cancer deaths from EPA Assessment of Risks from
Radon in Homes (EPA 402-R-03-003).
** Comparison data calculated using the Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention's 1999-2001 National Center for Injury Prevention and
Control Reports. |
I
am a licensed Radon Specialist,
I offer
Radon surveys as a stand-alone item without a home
inspection.
Order
a Home Inspection
Order a Radon Survey
Order an Energy Efficiency Audit
See what the US
Department of Health and Human Services
has to say about the dangers of Radon:
USDHHS
on Radon


I adhere
to the NACHI Standards of Practice
and the NACHI Codes of Ethics.
NACHI Standards of Practice
NACHI
Code of Ethics
Proudly
Serving the Following Counties:
Ada, Adams, Boise, Canyon, Gem, Payette,
Valley, Washington and Malheur
Oxbow Home Inspections • PO Box 2144 Eagle, ID 83616• 208.573.5300
Troy Farmer: Owner/Inspector • E-Mail: info@troyfarmer.com
© 2007- 2010 Oxbow Home
Inspections and Radon Testing, LLC





